
Finding the masses of molecules and ions
Using Ar values to work out the mass.
Ar values of elements
The table shows some Ar values:
Element Relative atomic mass
Hydrogen (H) 1
Carbon (C) 12
Oxygen (O) 16
Magnesium (Mg) 24
Chlorine (Cl) 35
For example:
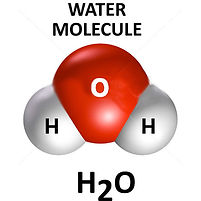
Hydrogen gas is made of molecules. Each molecules contain Each water molecule contains 2 hydrogen atoms and 1 oxygen
2 hydrogen atoms, so its mass is 2 (2x1=2) atom, so its mass is 18 (2x1+16=18)
Relative formula mass
Relative atomic masses can be used to find the relative formula mass of a compound.
To find the relative formula mass (Mr) of a compound, you add together the relative atomic mass values (Ar values) for all the atoms in its formula.
The masses of atoms,molecules, and ions
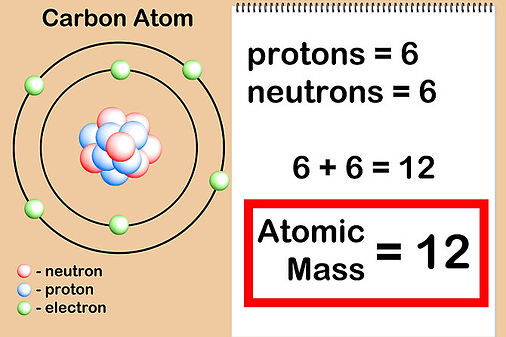
A standard carbon atom.
A single atom weighs almost nothing, therefore you can't use scales to weigh it so the scientist have to choose an atom of carbon-12 to be the standard atom. They fixed its mass as exactly 12 atomic mass units, then they compared all the other atoms with this standard atom by using a machine called a mass spectrometer.
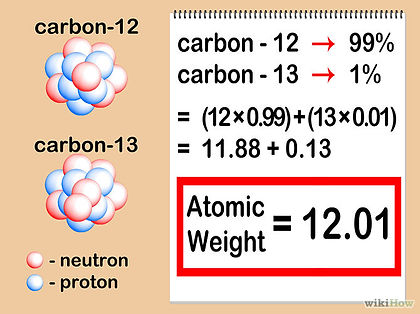
RELATIVE ATOMIC MASS
The relative atomic mass, Ar, for an element is the average mass of its naturally-occuring isotopes, relative to the mass of a carbon-12 atom.
R.A.M = mass of WESYWTM/mass of H

For example:

Substance Formula Atoms in formula Ar of atoms Mr
Ammonia NH3 1N N=14 1x14=14
3H N=1 3x1=3
Total=17
Magnesium Mg(NO3)2 1Mg Mg=24 1x24=24
2N N=14 2x14=28
6O O=16 6x16=96
Total= 148
